The idea of evaluating tanks from the Second World War — that is, from the early 1940s — according to the standards of the 1980s might seem extremely strange.But this is exactly idea that came to the minds of military theorists in the Soviet Union, who in the same 1980s conducted and published a corresponding assessment of Soviet and German tanks.
This was reported in blog „btvt _info” by military historian of armored vehicles Andriy Tarasenko. If you read his publication carefully, you can conclude that, apart from the ideological sense, the comparison of World War II tanks may have had practical meaning as well — but more on that below.
Read more: Ukrainian Tankers Reveal How They Fight on T-64: What Targets Tanks are Destroying, Realities of Modern Battlefield

More specifically, a comparison of the technical level of Soviet and German tanks from the Second World War was published in one of the issues of the journal „Questions of Defense Technology” dated 1986.
The authors of this comparison pointed out in the introduction that applying the 1980s methodology for evaluating armored weapons is objectively unsuitable for assessing tanks from the 1940s — particularly due to the emergence of new types of anti-tank weapons, changes in battlefield factors, and a radical shift in the technological level of the tanks themselves.
However, purely for the sake of an intellectual experiment, it was still possible to apply the 1980s methodology with certain simplifications to the tanks of the 1940s, calculating only three indicators: combat capabilities (Кб), mobility level (Кп), and the tank's technical level (Кт.у). Interestingly, the reference point for the Кт.у indicator was the T-34-76 model of 1940. The results of the comparison by tank types and modifications are shown in the table above.
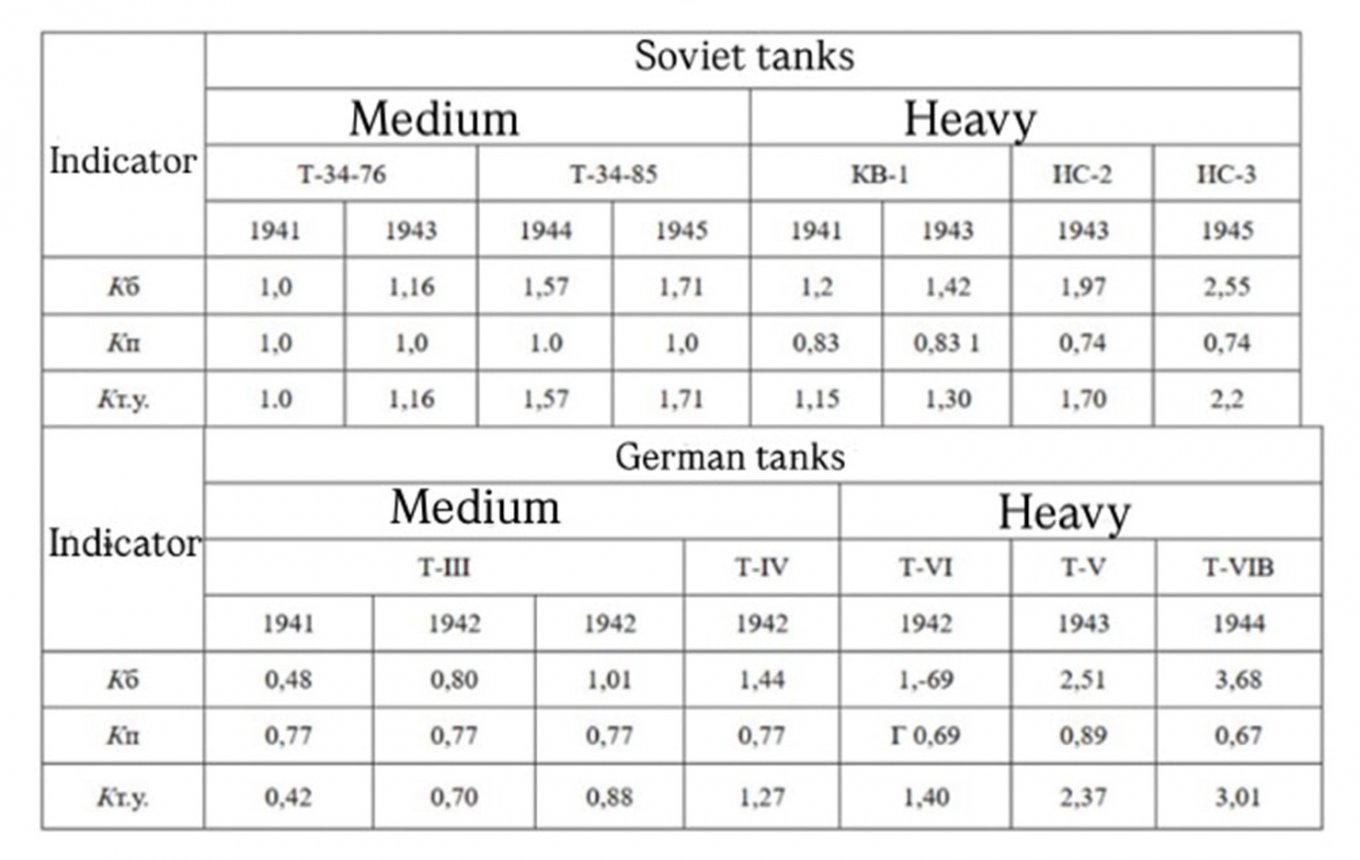
It is acknowledged that the evaluation of German tanks of the Pz III and Pz IV types was somewhat simplified, as between 1941 and 1943, German engineers created almost 10 modifications of the former and a comparable number of the latter.
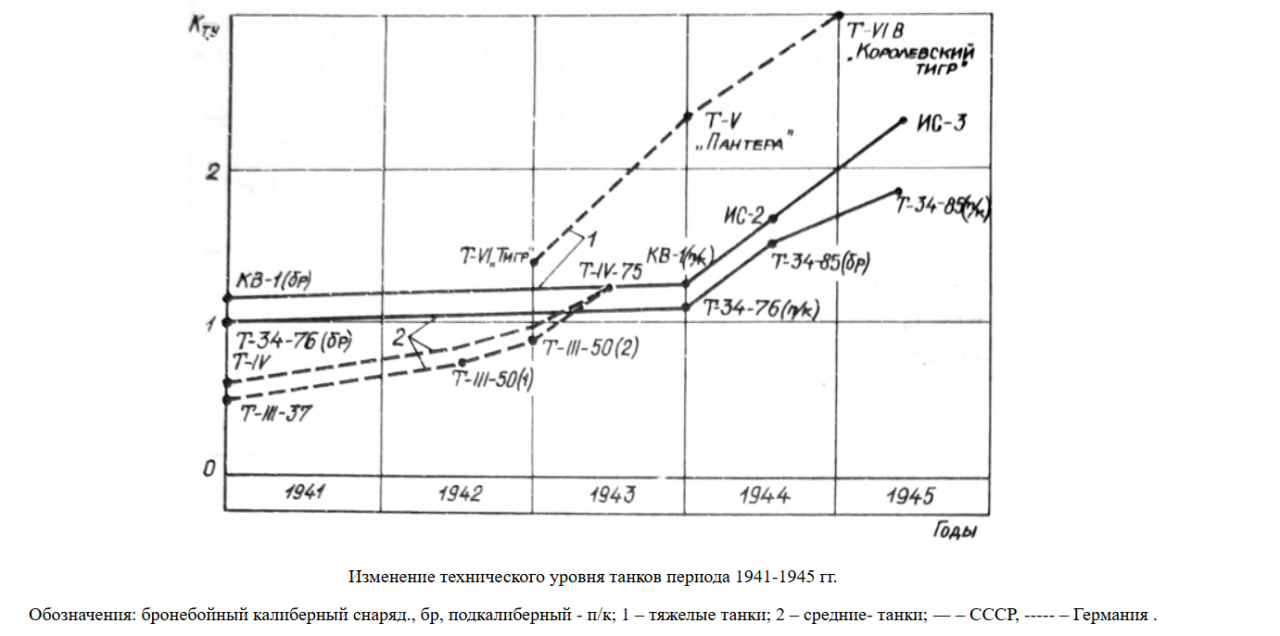
Also noteworthy is the provided diagram showing changes in the technical level of Soviet and German tanks. This diagram includes the recognition that after 1943, the medium and heavy tanks of the German Wehrmacht technically outperformed the medium and heavy tanks of the Red Army.
From Defense Express, we want to emphasize that although this theoretical comparison was conducted as late as 1986, some of the mentioned tank models were still in use.
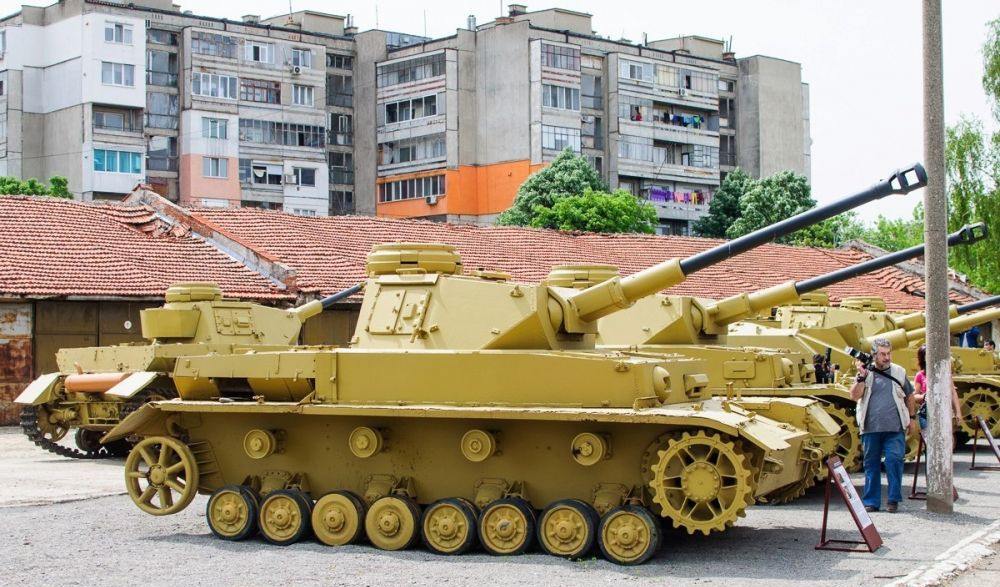
For example, the T-34-85 was officially retired from the Russian army only in 1993. As of the mid-1980s, IS-3 tanks were still officially in storage in reserve tank divisions in the Far East, and Bulgaria used Pz IV tanks as stationary firing points on the fortified "Kral Marko" line.

Another point — the above comparison of the technical levels of Soviet and German tanks may have served not only as an element of ideological justification for the Soviet victory in World War II, but also had a practical purpose for the Soviet military leadership. It helped justify the perspective that mass-produced tanks were more important than high-tech ones.
Read more: Ukrainian Tankers First Officially Spoke About Their Combat Work on Polish PT-91 Twardy Tanks














