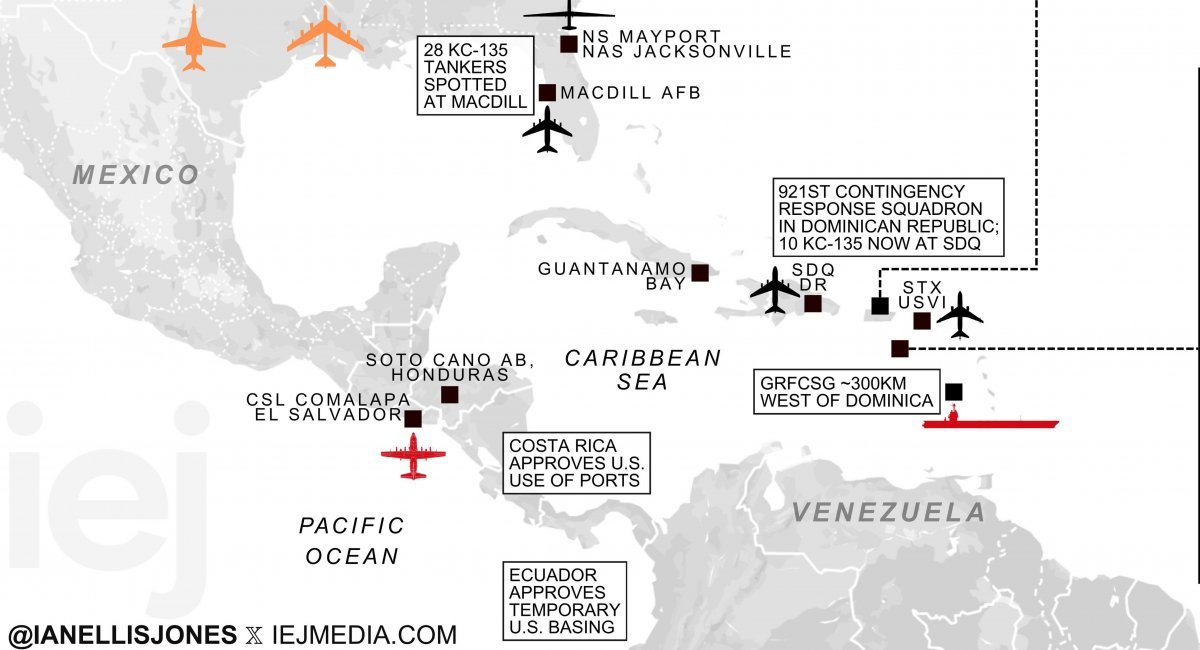
The launch of a full-scale U.S. operation against Venezuela can still be considered unexpected, even though the concentration of U.S. forces in the region has been ongoing since September 2025.
During this time, the U.S. has introduced the practice of destroying motor boats with crews suspected of transporting drugs, and since December 17, 2025, it has implemented a partial naval blockade of Venezuela to counter oil exports from the country by intercepting tankers subject to sanctions. On December 24, 2025, a limited attack was carried out on the port infrastructure of one of the drug cartels.
Read more: U.S. Launches Operation Against Venezuela, Caracas Under Attack, russian Air Defense Systems Neutralized, Landing Underway
Overall, a full-scale operation was expected, but due to the very long period of U.S. forces in the region, the escalation still came as an unexpected surprise, primarily for the Venezuelan armed forces.
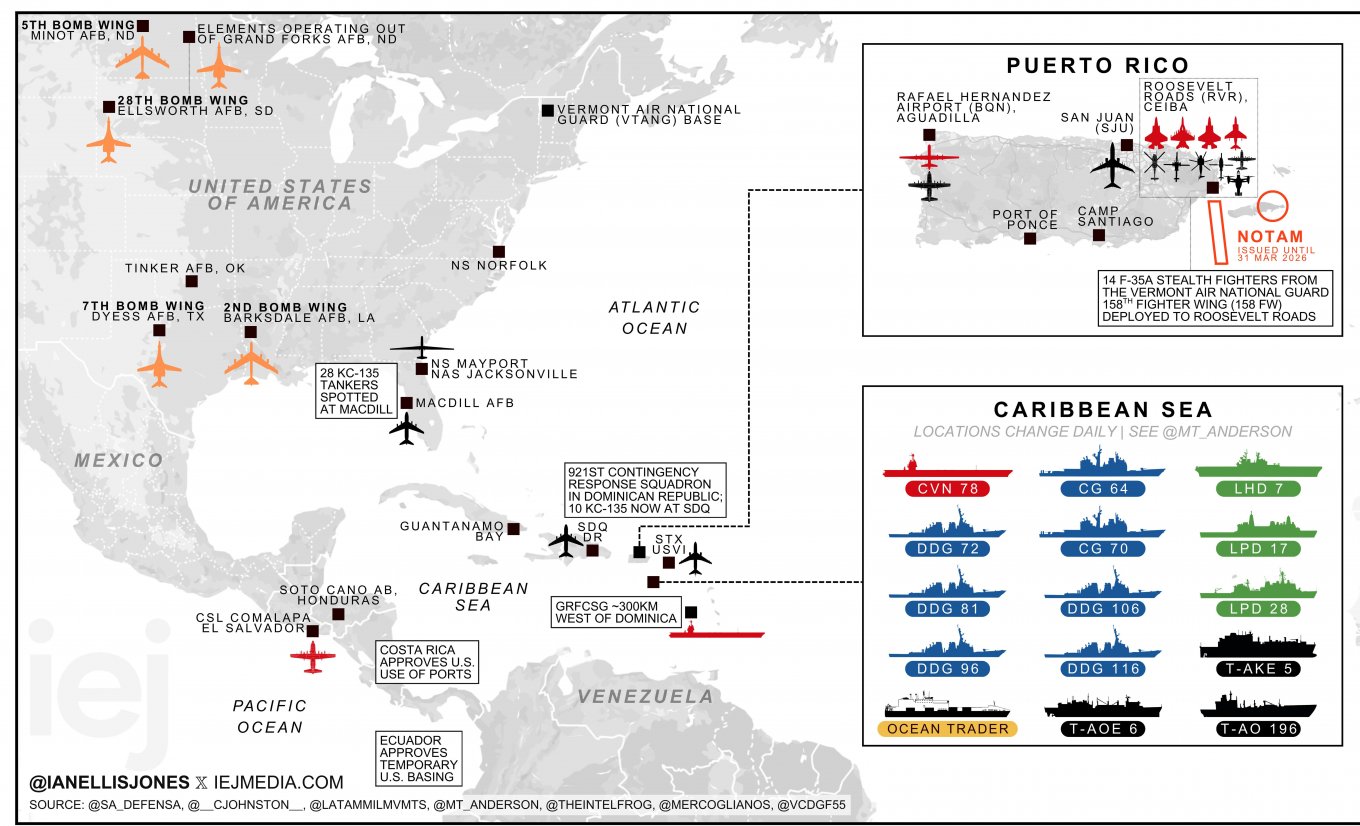
It is also important to outline the known U.S. forces that have been deployed. A preliminary assessment was made by analyst Jan Ellis in late 2025. At the same time, it should be noted that over the course of more than a week, the Pentagon may have concentrated additional forces, especially given the relatively short distance from the continental United States.
As the U.S. enforces & expands its blockade, additional strike & support assets arrived in SOUTHCOM:+ 14 VTANG F-35As deployed to Puerto Rico+ 921st Contingency Response Squad @ SDQ+ USAF U-28A Draco, EC-130H Compass Call, MC-130JPer POTUS, M/T Bella 1 is still on the run. pic.twitter.com/vgZuwQ71O5— Ian Ellis (@ianellisjones) December 23, 2025
At a minimum, the following carrier strike group can be considered the core of the deployed forces:
- led by the newest USS Gerald R. Ford (CVN-78) aircraft carrier;
- two Ticonderoga-class guided-missile cruisers: USS Gettysburg (CG-64) and USS Lake Erie (CG-70);
- five Arleigh Burke-class guided-missile destroyers: USS Stockdale (DDG-106), USS Gravely (DDG-107), USS Mahan (DDG-72), USS Winston S. Churchill (DDG-81), and USS Bainbridge (DDG-96);
- two Virginia-class nuclear-powered attack submarines.
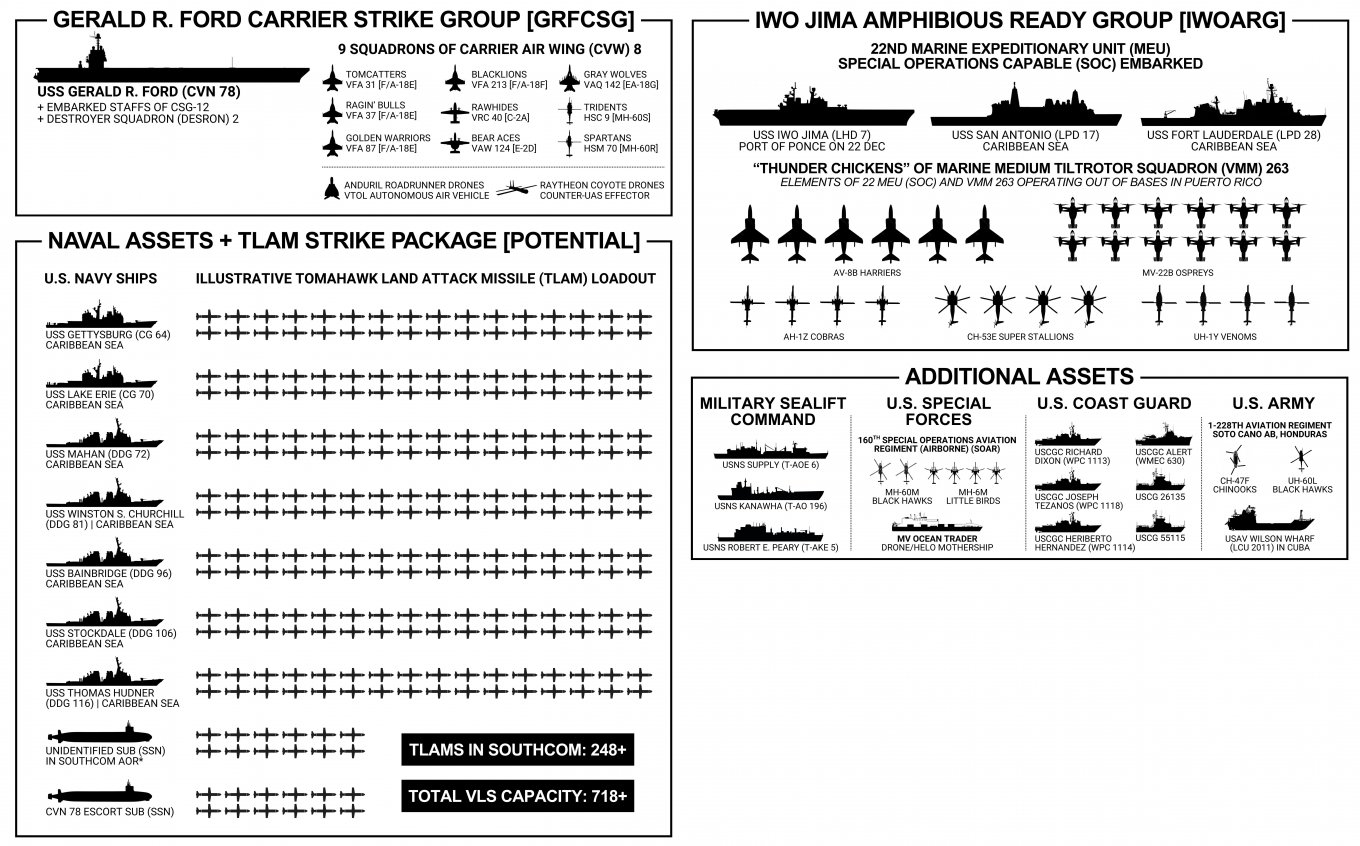
In addition, an amphibious task force is operating in the region. It includes USS Iwo Jima (LHD-7), a Wasp-class amphibious assault ship, as well as two San Antonio-class amphibious transport docks: the lead ship USS San Antonio (LPD-17) and USS Fort Lauderdale (LPD-28). These forces are also supported by a U.S. special operations forces support vessel.
Separate U.S. forces have been deployed to Puerto Rico. These include the 158th Fighter Wing of the Vermont Air National Guard, equipped with F-35 fighters (not shown on earlier infographics, as they arrived later). They joined the 225th Marine Corps F-35B squadron and the 132nd squadron of E/A-18G electronic warfare aircraft. There is also information about the deployment of MQ-9 Reaper UAVs and even an AC-130 "flying artillery battery", as well as appropriate support forces in the form of air tankers and P-8 patrol aircraft.
Naturally, any operation against Venezuela can also be reinforced by aviation units based in the continental United States. First and foremost, this includes the 2nd, 5th, 7th, and 28th Bomb Wings, which operate B-1B and B-52 strategic bombers. In addition, air bases within the United States itself can be used to conduct strikes against Venezuela with tactical aircraft, supported by aerial refueling.
Read more: Venezuela Deploys Iranian Mohajer-6 Drones, Already Used Against Ukraine, to Target U.S. Naval Vessels